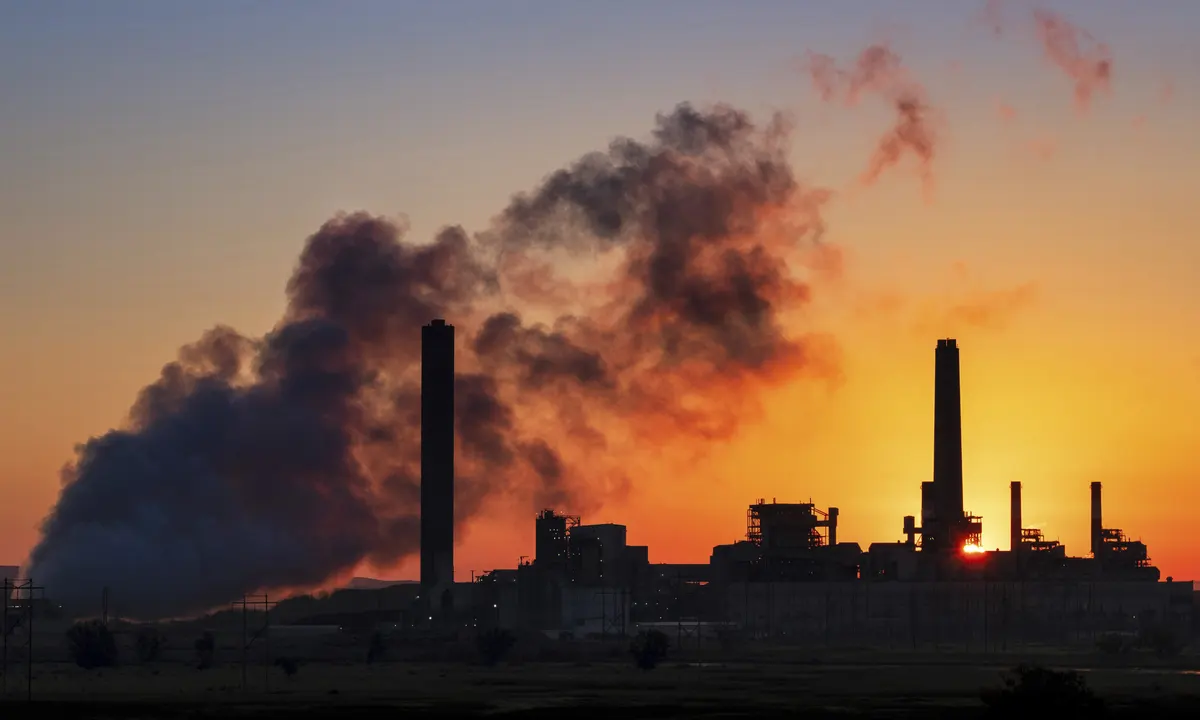
With the Paris Agreement coming into effect, many countries are pledging to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. China, however, plans on going in the opposite direction. In fact, they plan on accelerating the construction of coal-fired power plants! What’s behind this drastic change in policy?
China is facing a number of challenges as it tries to transition to a more sustainable economy. Chief among these is the need to find new sources of energy. Coal has been a major part of China’s energy landscape for centuries, and it’s still the dominant source of electricity in the country. However, coal-fired power plants are a major contributor to climate change, and Beijing knows that they need to find alternatives if they want to meet its emissions targets.
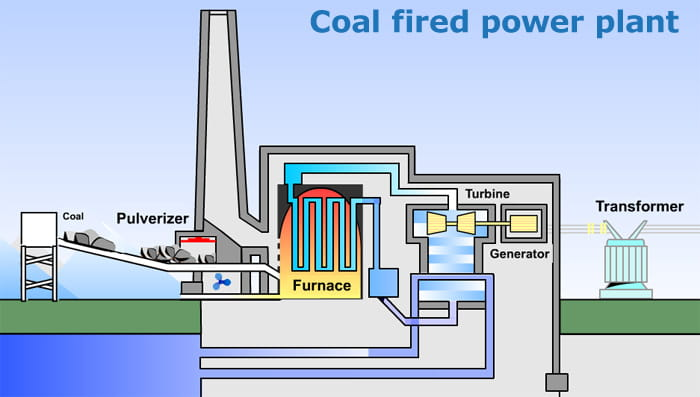
Table of Contents
China Plans To Accelerate The Construction Of Coal-Fired Power Plants
China plans to accelerate the construction of power plants in order to meet the rising demand for energy. Coal is the main source of energy for China, and the country has been increasing its reliance on it in recent years.
The government plans to build 54 new power plants by 2020. This will increase China’s total coal-fired power capacity by about 25%. The new plants will help to address China’s growing energy needs and environmental concerns.
The problem with coal is that it emits a lot of pollutants. These pollutants can cause health problems, climate change, and air pollution. China is aware of these problems and is working to find alternative sources of energy.
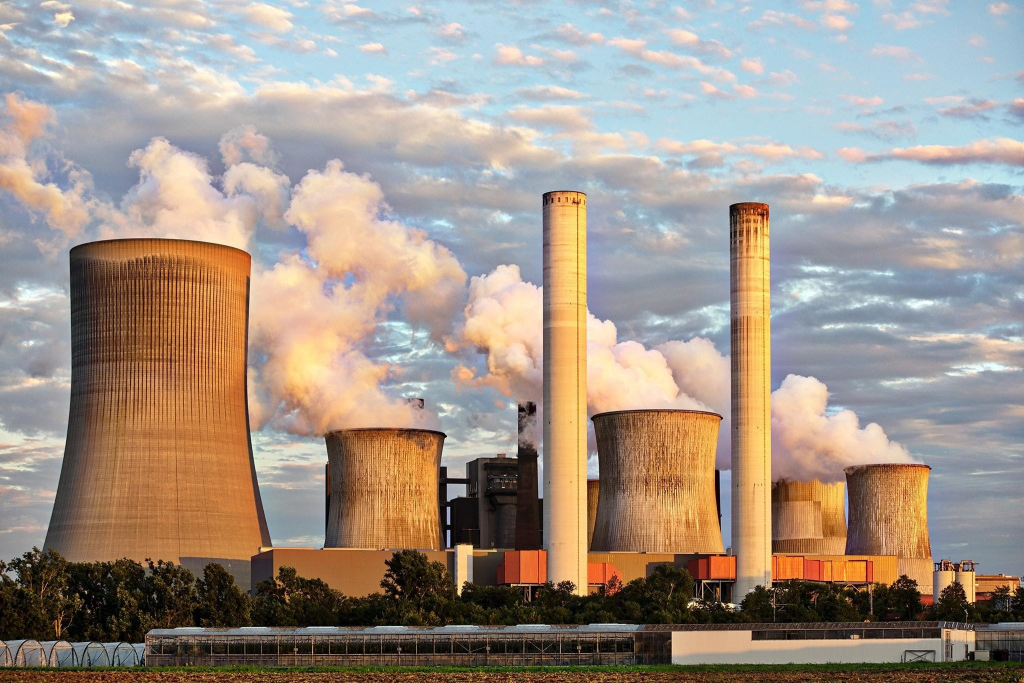

Environmental Concerns With Coal-Fired Power Plants
The Chinese government has announced plans to accelerate the construction of coal-fired power plants, despite environmental concerns. Coal is the most polluting form of energy, and this new development could have significant consequences for the environment.
Coal-fired plants release large amounts of greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide. They also produce harmful air pollutants such as mercury and arsenic. These pollutants can damage human health and contribute to climate change.
The Chinese government has acknowledged these concerns, but it remains committed to expanding the use of coal-fired power plants. This decision could have serious consequences for the environment and human health.
Benefits of Coal-Fired Power Plants
China plans to accelerate the construction of power plants in order to improve air quality and lower energy costs. The country has been struggling with high levels of air pollution, which has led to health concerns and economic losses. Coal-fired plants produce less smog and other pollutants than other forms of energy, such as gas or solar. In addition, they are more affordable than other types of power generation.
The government is also hoping that the new plants will help reduce China’s reliance on imported oil. Coal-fired power plants use less energy than other forms of power, making them a good option for countries with limited resources.
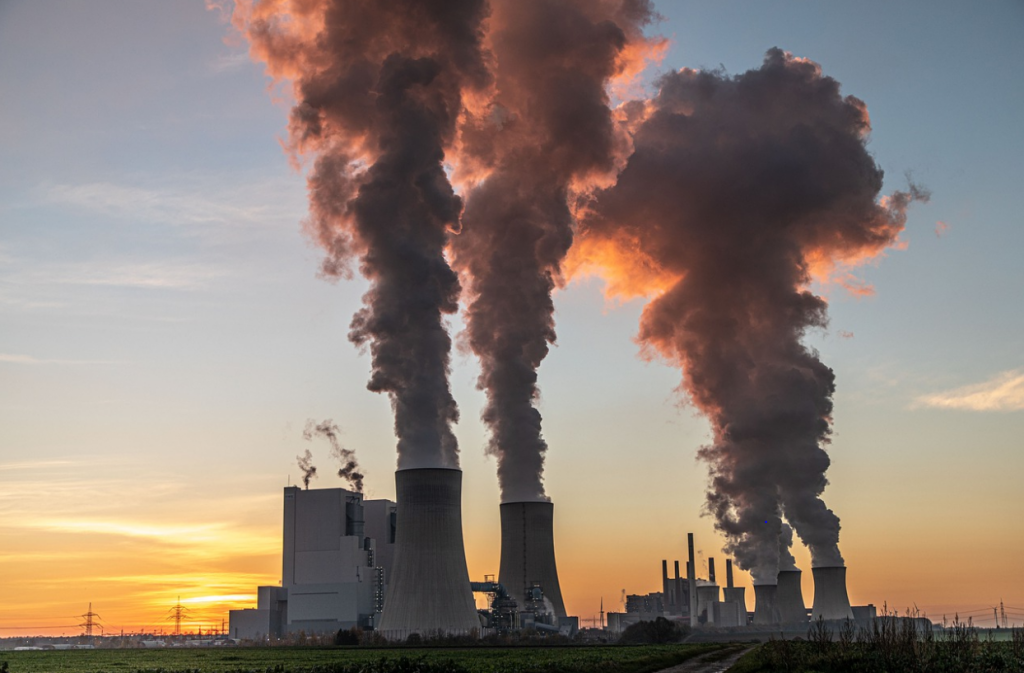

Despite these benefits, some environmental groups have voiced concerns about the impact of coal-fired power plants on climate change. Coal is one of the most carbon-intensive sources of energy, and burning it to generate electricity releases large amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Conclusion
China plans to accelerate the construction of power plants in an effort to meet rising energy demands and reduce its reliance on imported oil. The country has already invested billions of dollars in new coal-fired power plants, and these investments are expected to continue as Beijing strives to become a global leader in clean energy. However, while this move will help China achieve its goals, it is also likely to have negative consequences for the environment and human health.